In this article:
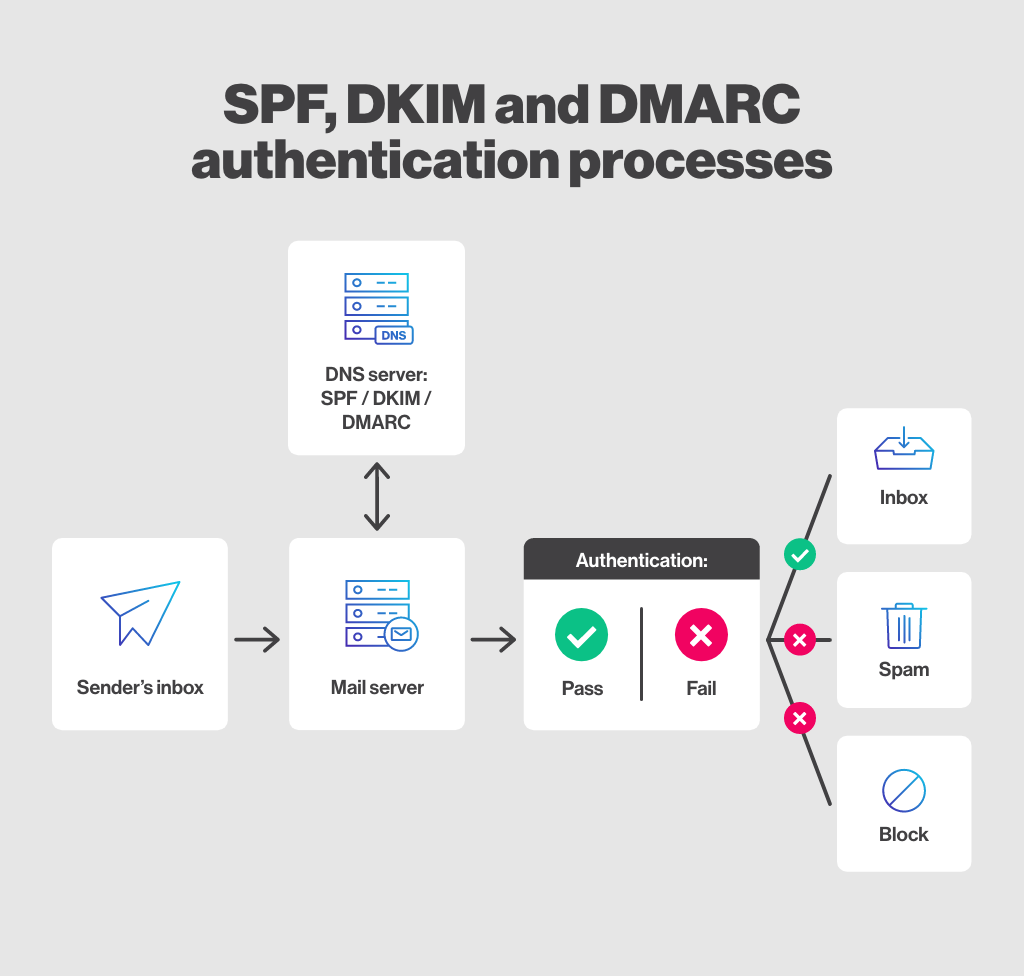
The implementation of SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) authentication on email sending domains is crucial to build trust, reduce phishing risks, protect against fraud, ensure the legitimacy of electronic messages, and improve email deliverability. By combining SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, organizations can establish a multi-layered approach to strengthen the security of outgoing emails.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
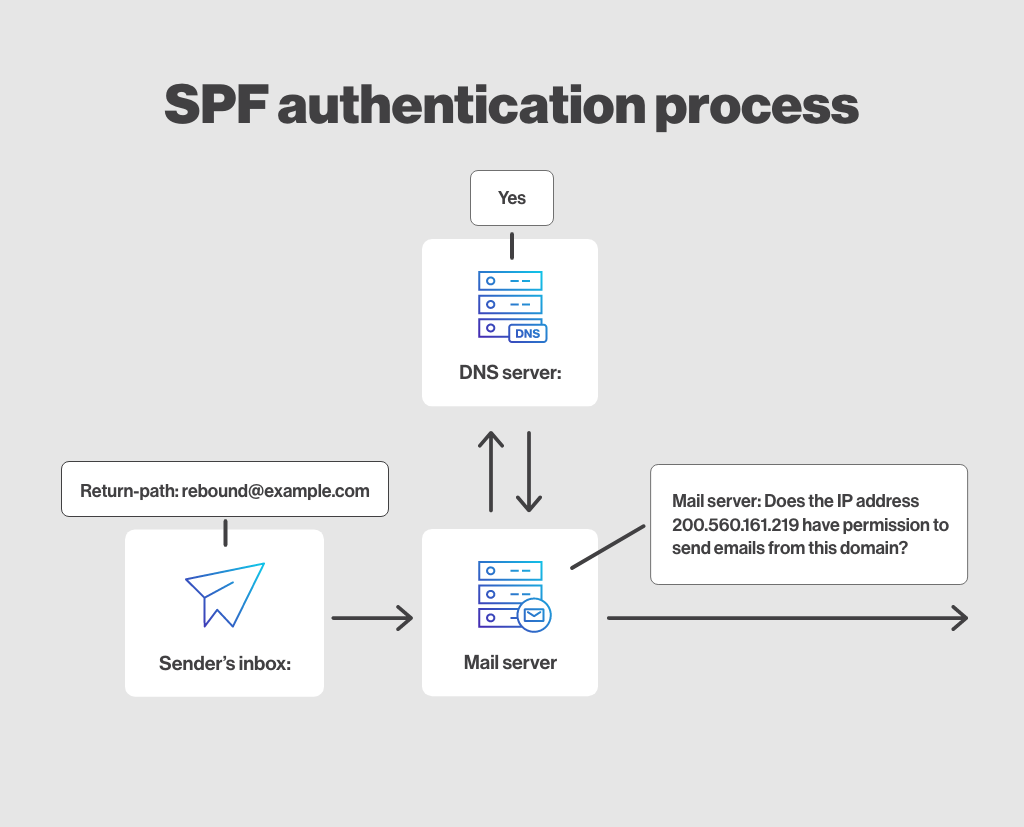
SPF allows the owners of a domain to specify the mail servers authorized to send email on its behalf. SPF authentication is verified on the domain of the "Return-path" address.
Why use SPF
SPF authentication protects against identity theft by preventing the sending of fraudulent emails from unauthorized servers. This helps ensure that emails are sent by legitimate sources.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
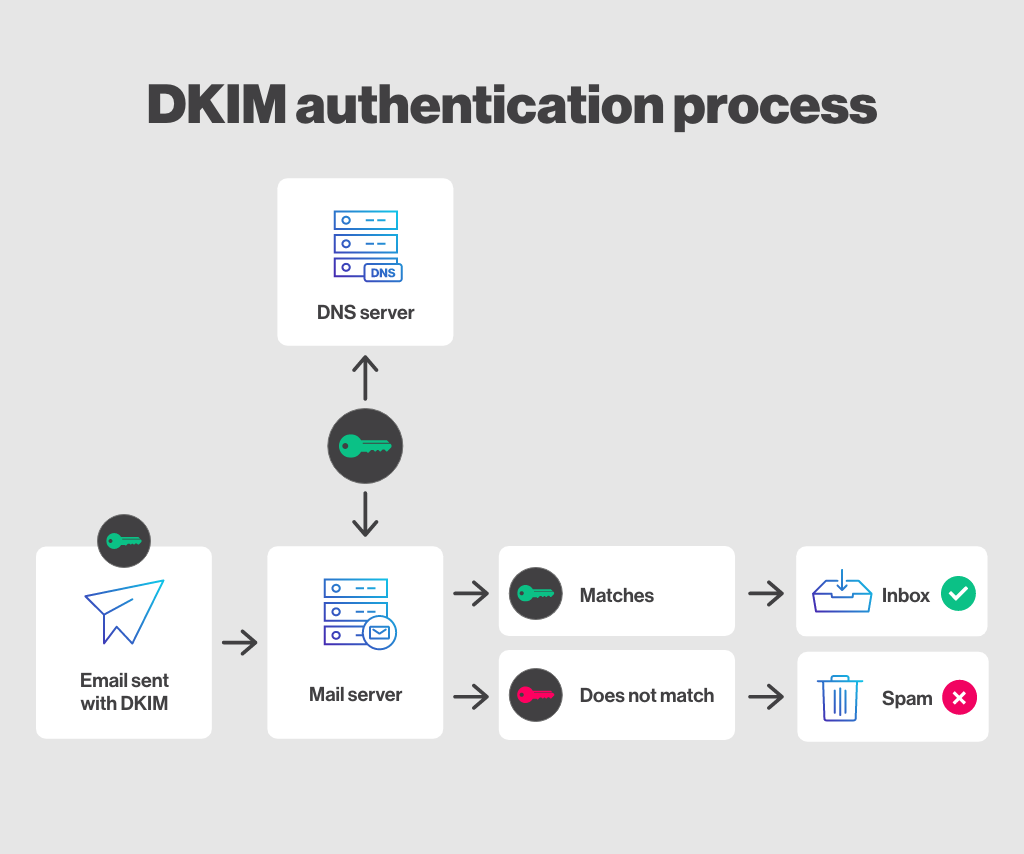
DKIM is an email authentication method that allows the sender to use a digital signature to associate the message with their domain.
Why use DKIM
This signature (DKIM) is included in the headers of an email and is used to verify that the email was indeed sent by the claimed domain and has not been altered in transit. It also helps combat content forgery and strengthens recipient trust.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)
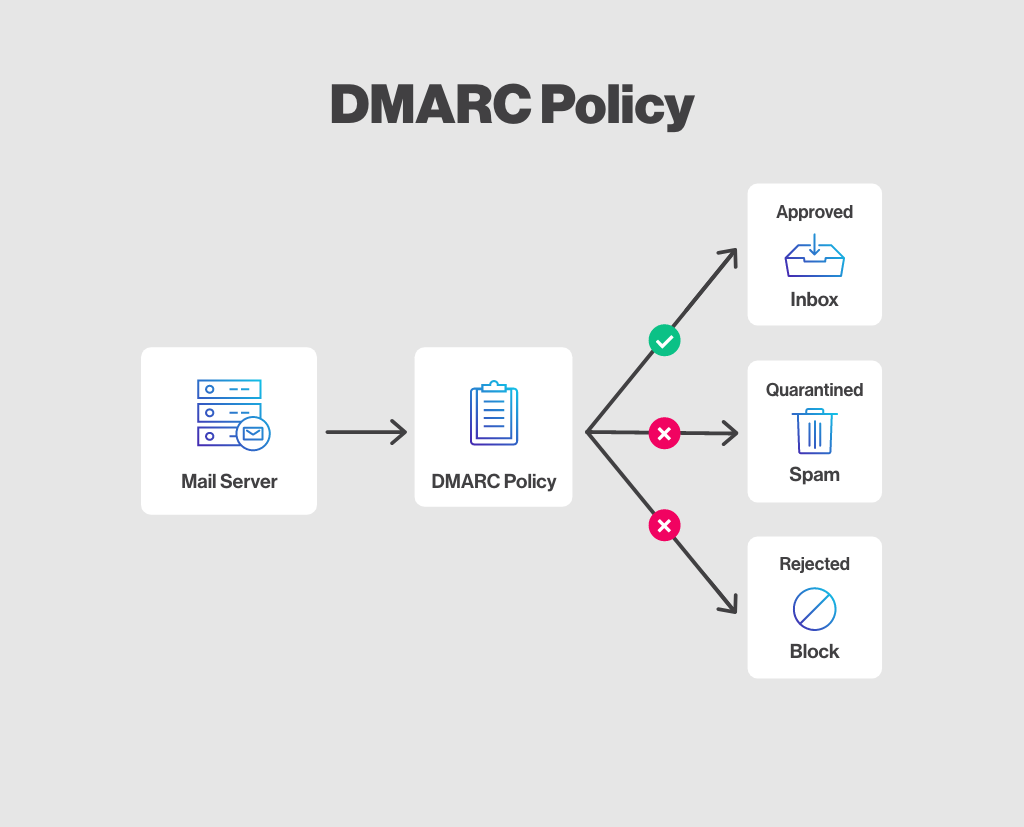
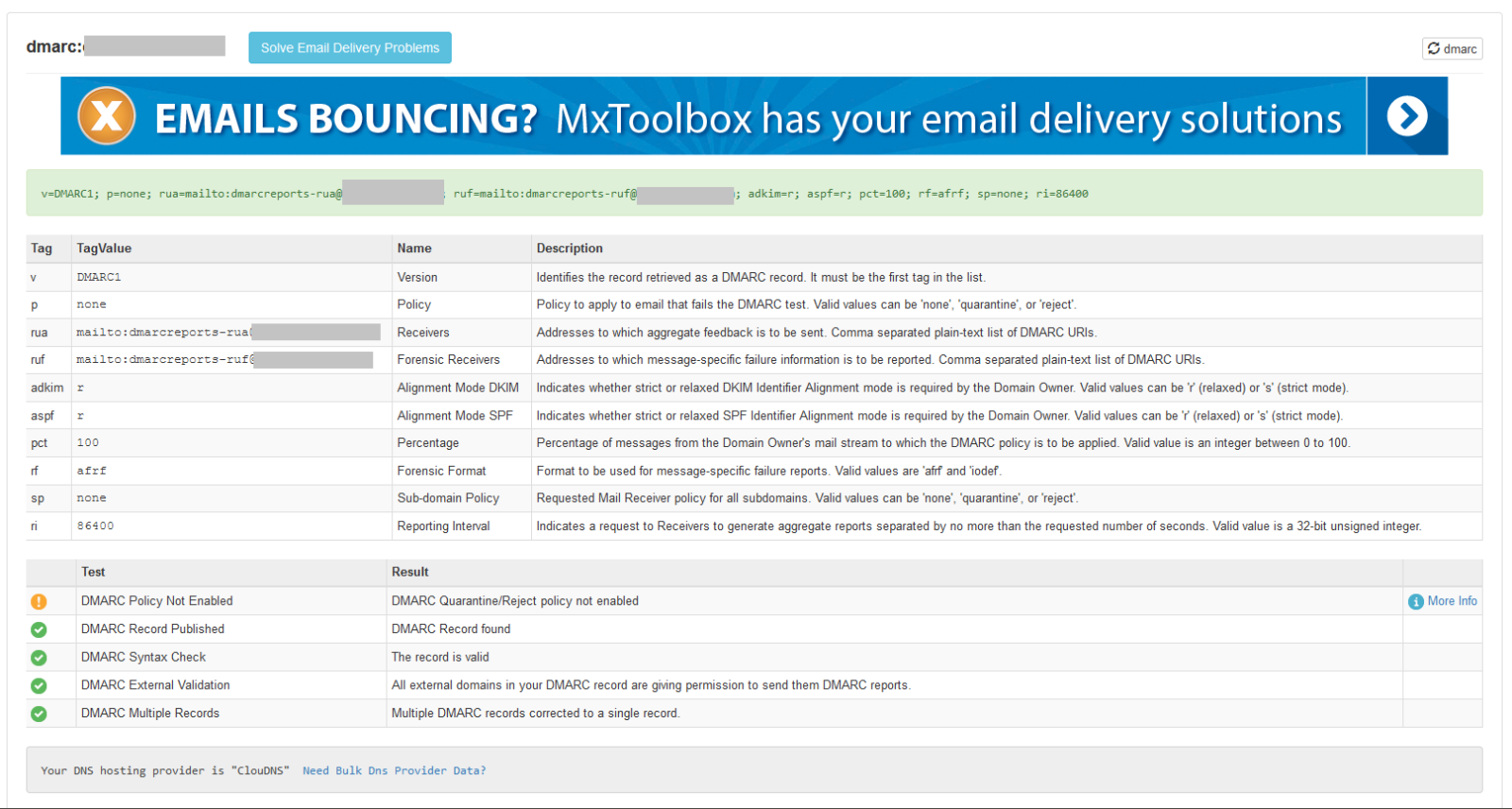
DMARC is an authentication method for ensuring that messages sent from your email address really do come from you, and for specifying to others how emails that fail authentication tests should be handled. For DMARC authentication to pass, the email must be correctly authenticated with SPF or a DKIM signature, and the domain in the "From:" field (the visible header) must match the one of the SPF authentication or DKIM signature (also known as SPF or DKIM alignment).
Why use DMARC
The DMARC policy complements SPF and DKIM by providing an authentication policy for the domain. It helps define actions to be taken for emails that fail SPF and/or DKIM checks, such as quarantining or rejecting them. If someone tries to forge your email address, this will prevent forged emails from reaching their destination and damaging your reputation. Additionally, DMARC allows you to receive detailed reports on identity spoofing attempts if you include an email address in your record to receive them.